Best Root Cause Analysis Software
This document examines best practices for using root cause analysis (RCA) to improve patient safety, and includes guidelines to help health professionals standardize the RCA process and improve the way they investigate medical errors, adverse events, and near misses. Download Our Free Root Cause Analysis Excel Template and Become A Better Problem Solver. One of the benefits of the Cause Mapping method is the ability to conduct thorough research and investigation of problems without purchasing new root cause analysis software. We teach clients how to document an entire investigation using a tool that is likely already on their computer - Microsoft Excel.
What is a Root Cause Analysis?
This is what applies to the core, while Software Testing and the best approach is Root Cause Analysis. How best can it be done and what are its apparent benefits, is what reflects in this article. Ideal software is the one with the least of bugs and the best of quality. It, is indeed, foolish to ask for a software with zero defects. Best Root Cause Analysis Tools and Methods You know that looking at symptoms of a problem is not enough to resolve it. You need to strike at the core of a problem by finding its key and root causes.
A root cause analysis is a means to get to the bottom of a problem or unexpected event. Root cause analyses are important to undertake when your project or product is not what was expected. Root cause analyses aim at improving products or processes – quality – and they must be undertaken in systematic ways in order to be effective. The general process for undertaking a root cause analysis are:
Game Board 50 Green Marker Chips 35 Red Marker Chips. 104 Sequence Cards 50 Blue marker Chips. When two players or teams are playing, use only blue and green marker chips. Red chips are used only when there is a third player or third team. Joker cards are not used in the play of the Sequence game. Sequence card game instructions for 3 players. The game of sequence is an exciting game of strategy. It is simple to learn and fun to play. The following are the sequence game rules. Players It can be played with two players or two teams. If playing in teams be sure to divide the players evenly. Alternate, players around the board, so that. Old school games have always been fun, and if it were to involve poker chips and cards - even better! We bring you the rules of the delightful 'Sequence' board game, along with some tips and strategy to play the game. Aug 14, 2017 Sequence is a deceptively simple board game, wherein the goal is to create a row poker chips or 'sequence' on the game board. With rules for up to 12 players, the game becomes a battle of strategy, wits and luck as you try to beat your opponents to the punch. 'Sequence' is a board and card game published by Jax Ltd. The standard version of the game is played with regular playing cards, but Jax Ltd. Also produces editions featuring geographic locations and simple math, in addition to a 'Sequence' dice game.
- Describe the problem your company is looking at
- Gather data associated with the problem
- Identify potential causes for the problem
- Identify which causes you will remove or change in order to prevent repeat problems
- Identify solutions that will be effective in preventing repeat problems
- Implement changes
- Observe changes to ensure that they have effectively eliminated the problem
The most comprehensive approach to problem-solving. Pin-point the most effective solutions during a root cause analysis with RealityCharting. This clear visual tool is invaluable in finding cause and effect relationships, leading your team to resolution faster. Root cause analysis may seem overwhelming at times, but it’s practice and application are vital for the success of your business. Without it, an organization won’t be able to reach its potential. However, using these tools, along with strong root cause analysis facilitation practices (look for a future blog post) will be a difference maker.
There are many techniques involved in a root cause analysis. You may already be familiar with the five whys analysis. Even if you aren’t, you will be familiar with it and many of the other types of root cause analysis techniques after reading the rest of this article.
Five Whys Analysis
This might sound like the technique of a five-year-old wanting to get out of going to bed, but the five whys analysis can be quite useful for getting to the underlying causes of a problem. By identifying the problem, and then asking 'why' five times – getting progressively deeper into the problem, the root cause can be strategically identified and tackled.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
The failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a technique aimed to find various modes for failure within a system. Many manufacturing companies utilize this technique. FMEA requires several steps to execute:
- All failure modes (the way in which an observed failure occurs) must be determined.
- How many times does a cause of failure occur?
- What actions are implemented to prevent this cause from occurring again?
- Are the actions effective and efficient?
Root Cause Analysis Free Software
FMEA is often performed and updated any time a new product or process is generated, when changes are made to current conditions, or to the design, when new regulations occur, or when there is a problem determined through customer feedback.
Pareto Analysis
The Pareto analysis operates using the Pareto principle (20% of the work creates 80% of the results). You will want to run Pareto analysis any time when there are multiple potential causes to a problem. In order to perform a Pareto analysis, you will want to create a Pareto chart using Excel or some other program. To create a Pareto chart, you will list potential causes in a bar graph across the bottom – from the most important cause on the left to the least important cause on the right. Then, you will track the cumulative percentage in a line graph to the top of the table. The causes reflected on the table should account for at least eighty percent of those involved in the problem.
Fault Tree Analysis
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is another method of getting to the root cause of a problem. An FTA uses boolean logic to determine the root causes of an undesirable event. This root cause analysis technique is often used in risk analysis and safety analysis. At the top of the fault tree, the undesirable result is listed. From this event, all potential causes tree down from it. Each potential cause is listed on the diagram in the shape of an upside down tree.
Current Reality Tree (CRT)
The current reality tree analyzes a system at once. It would be used when many problems exist and you want to get to the root causes of all the problems. The first step in creating a current reality tree is listing all of the undesirables or, problems. For example, you may have the following problems with your computer:
- The computer keeps crashing when using a particular program
- The computer often runs slow
- The computer sometimes randomly shuts off
- Items you save aren’t where you expect them to be
Now, what happens next is to begin a chart starting with each of those problems using causal language (if…and…then). The tree will depict each potential cause for a problem. Eventually, the tree will show one cause that is linked to all four problems.
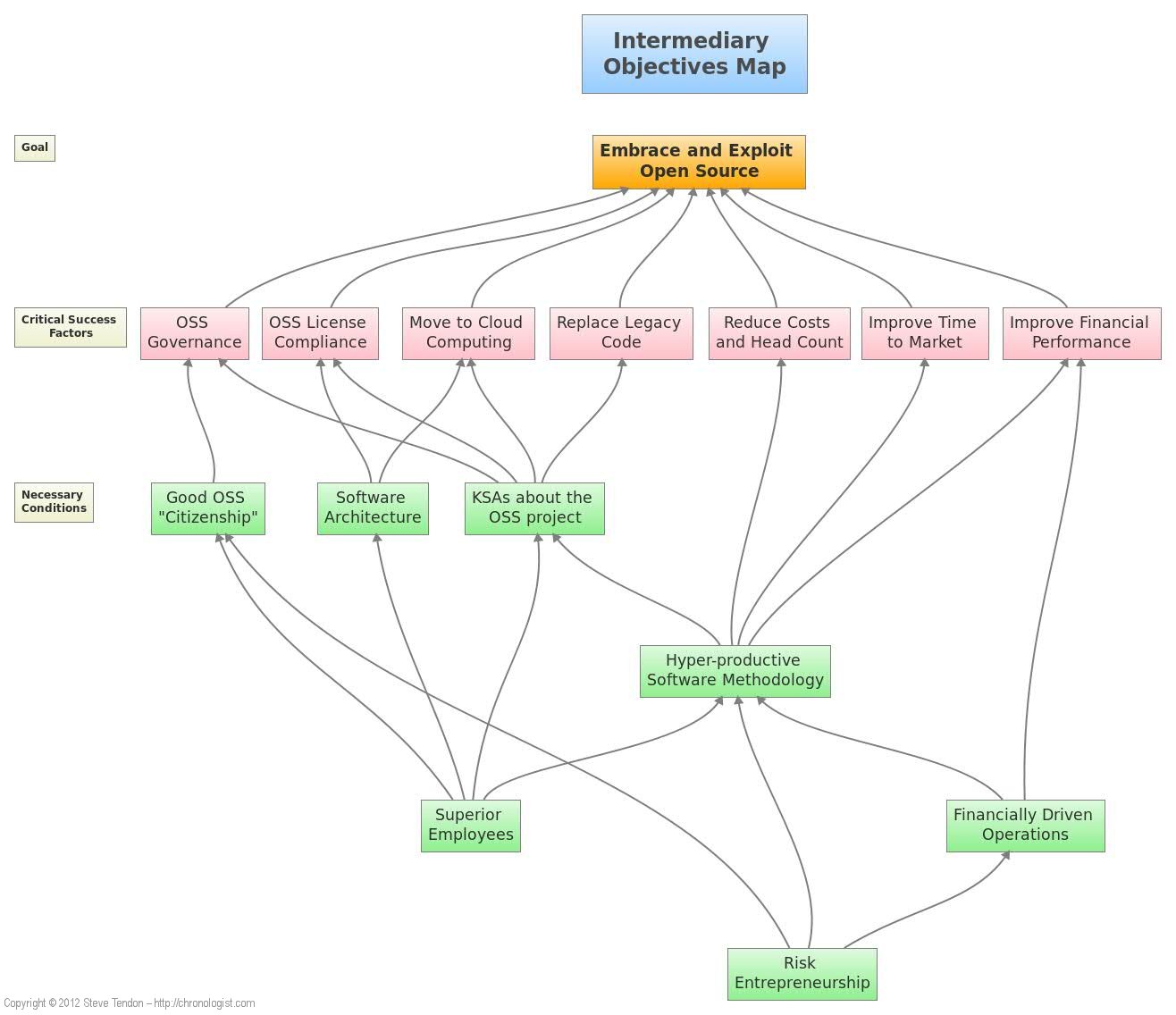
Fishbone or Ishikawa or Cause-and-Effect Diagrams
No matter what term you use for the fishbone diagram, the truth is, that it is a useful technique that will help you in your root cause analysis. A fishbone diagram will group causes into categories including:
- People
- Measurements
- Methods
- Materials
- Environment
- Machines
Best Root Cause Analysis Software Download
Depending on the industry you are in, you may use different categories such as The 4 M’s (manufacturing), The 4 S’s (service) or the 8 P’s (also service). The diagram gets its name due to the fact that it looks like a fishbone, with categorized causes and their sub-causes visualized.
Kepner-Tregoe Technique
The Kepner-Tregoe technique, also known as rational process is intended to break a problem down to its root cause. This process begins with an appraisal of the situation – what are the priorities and orders for concerns for specific issues? Next, the problem analysis is undertaken, where an analysis is undertaken to get the cause of undesired events. Then, a decision analysis is tackled, outlining various decisions that must be made. Finally, a potential problem analysis is made to ensure that the actions decided upon in step three are sustainable.
RPR Problem Diagnosis
One final technique used in root cause analyses is the RPR Problem diagnosis. RPR stands for 'Rapid Problem Resolution' and it deals with diagnosing the causes of recurrent problems. This process has three phases:
- Discover – team members gather data and analyse their findings
- Investigate – a diagnostic plan is created and the root cause is identified through careful analysis of the diagnostic data
- Fix – the problem is fixed and monitored to ensure that the proper root cause was identified.